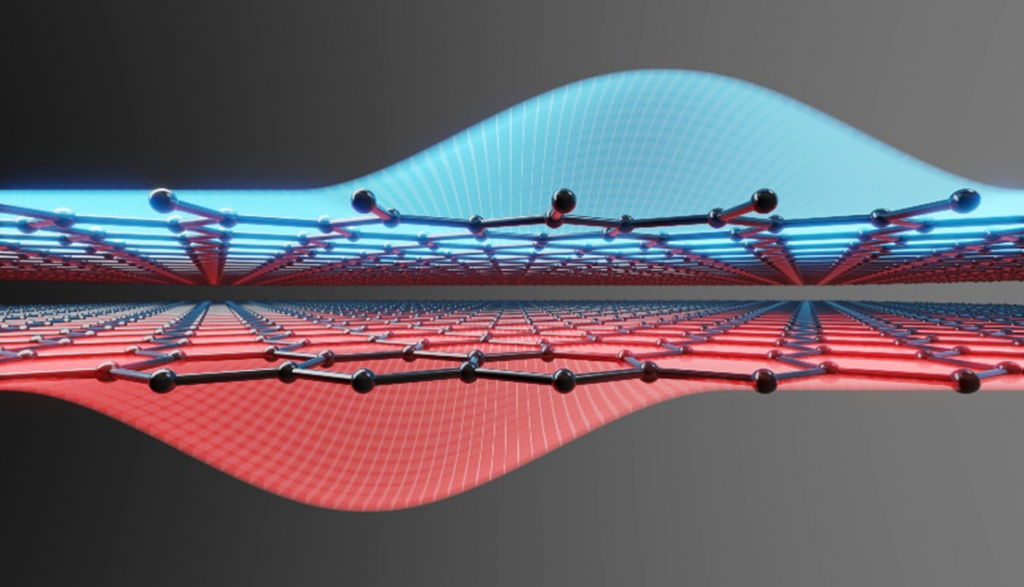
Researchers of the Aachen Graphene and 2D Materials Center have demonstrated the first CMOS inverter based on transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDC) on a flexible substrate, using two distinct TMDC materials, MoS2 and WSe2.
Continue reading “First demonstration of a CMOS inverter based on transition metal dichalcogenides on a flexible substrate”An effective method to measure the adhesion of 2D materials
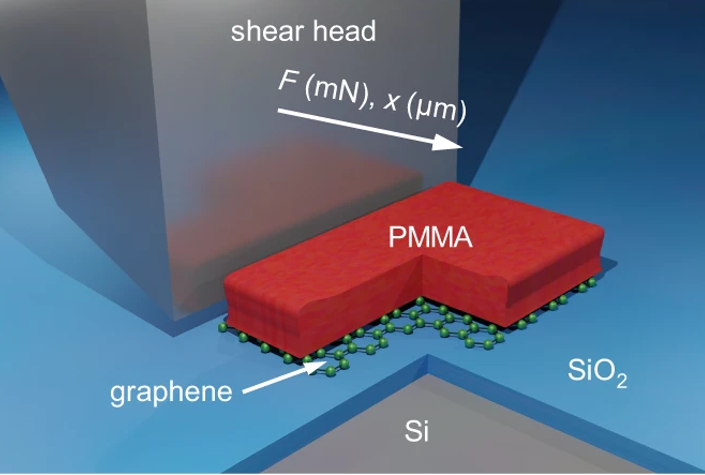
One of the big selling points of two-dimensional (2D) materials is their self-passivated nature, which allows them to be deposited on any substrate and opens up new possibilities for three-dimensional material stacks. The downside is their weak adhesion to the substrate, which can be a source of device instability. Quantifying the adhesion of 2D materials to three-dimensional surfaces is therefore an essential step for the reliable integration of devices based on 2D materials. A team of researchers around Max Lemme has now shown that the adhesion between 2D materials and substrates can be efficiently quantified using button-shear testing.
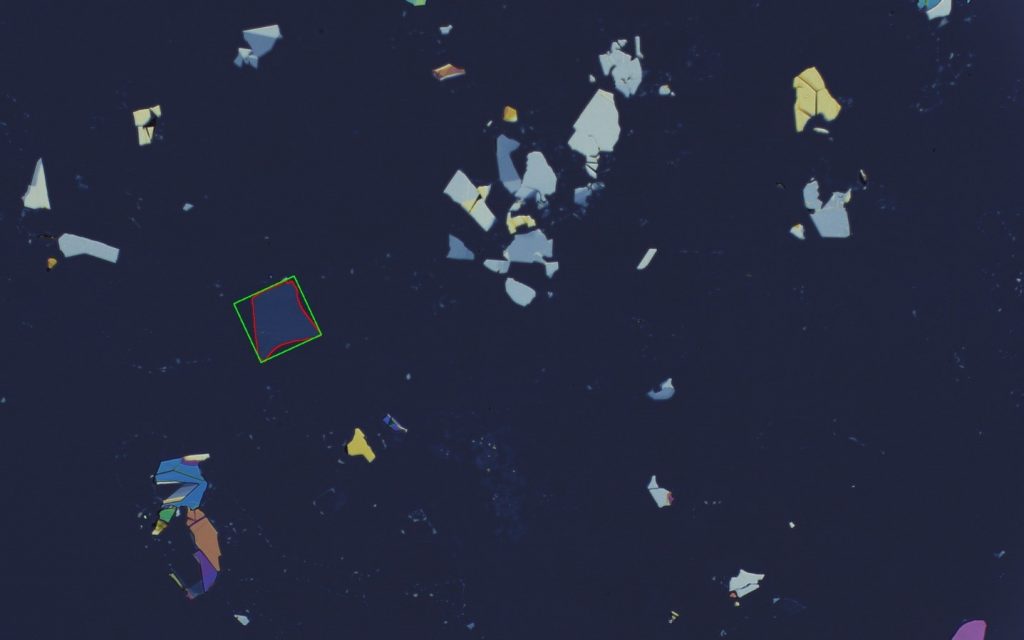
An automatic flake-search tool for 2D materials
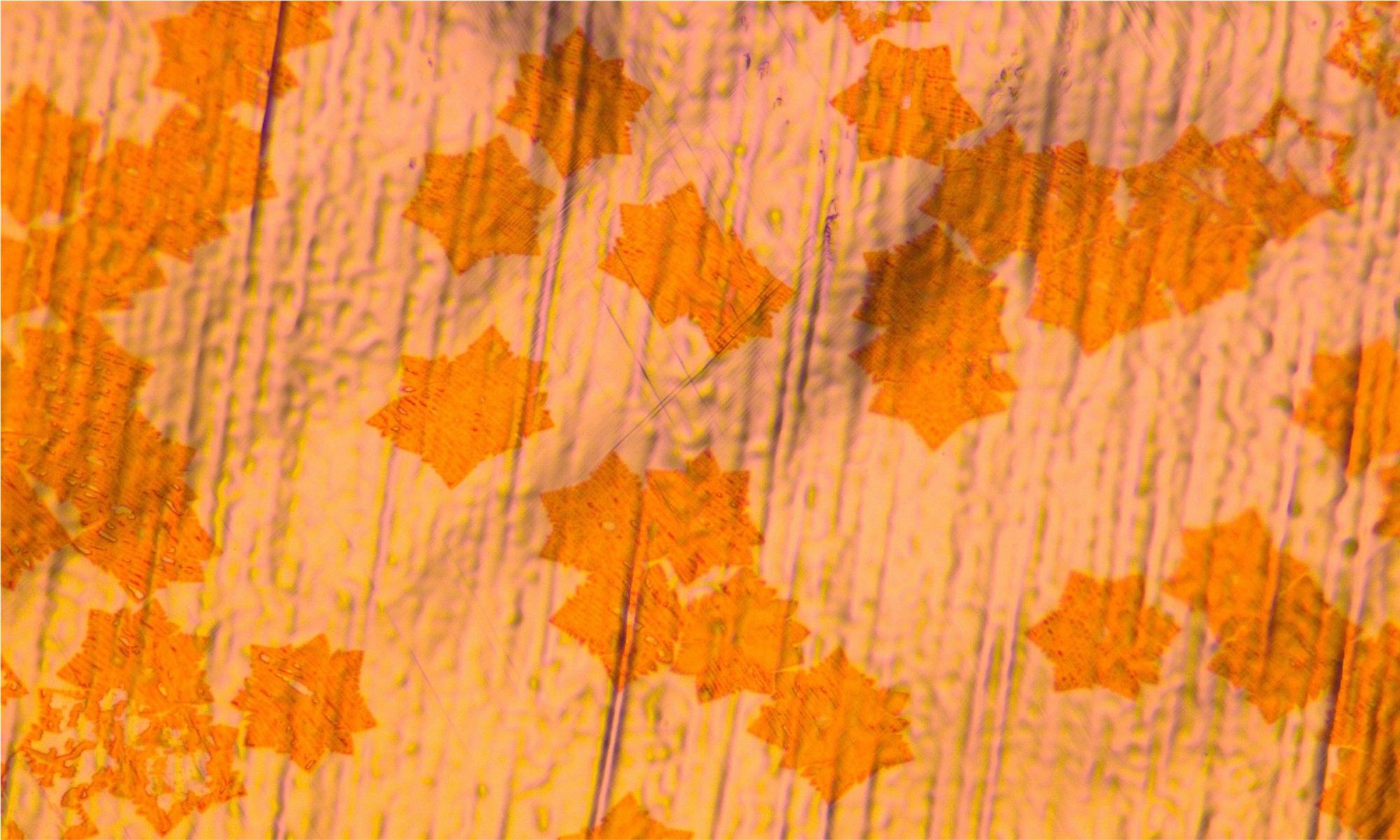
Researchers at the Aachen Graphene & 2D Materials Center have released an open-source platform to automatically identify and classify exfoliated flakes of two-dimensional (2D) materials on a substrate, shortening one of the most time-consuming and tedious tasks in the study of 2D materials.

A workshop in Aachen on “2D Materials for Future Electronics”
AMO GmbH and the Aachen Graphene & 2D Materials Center are organizing a two-day workshop on “2D Materials for Future Electronics”, in cooperation with RWTH Aachen University and the University of Wuppertal.

First observation of coherent charge dynamics in graphene quantum dots
In a recent study published in Nature Communications, researchers from RWTH Aachen University and Forschungszentrum Jülich have reported the observation of coherent charge oscillations in bilayer graphene quantum dots. This marks a significant milestone on the way to spin and valley qubits in a two-dimensional material system.

High quality hexagonal Boron Nitride – made in Aachen
Good news for the community working on two-dimensional materials in Europe: a team of researchers at RWTH Aachen University has successfully implemented the process for growing high-quality hexagonal Boron Nitride at atmospheric pressure and high temperature, increasing the resilience of the supply chain of this unique material.

Congratulations to Prof. Annika Kurzmann
Prof. Annika Kurzmann has been appointed ML4Q Professor for Experimental Solid-State Physics at the University of Cologne.
Continue reading “Congratulations to Prof. Annika Kurzmann”Interlayer transfer of valley polarization from excitons to free charge carriers in WSe2/MoSe2 heterobilayers
Scientists from RWTH Aachen, AMO GmbH, Forschungszentrum Julich and the University of Regensburg have shown that in twisted heterobilayers of WSe2 and MoSe2 there is a transfer of valley polarization from excitons in WSe2 to free carriers in MoSe2. This mechanism, which is strongly dependent on the twist angle, may allow the realization of opto-valleytronic devices where the valley polarization is optically excited but extracted and measured by electrical means. The results are reported in npj 2D Materials and Applications.

Congratulations to Prof. Alwin Daus
Alwin Daus has been appointed Junior Professor at the Department of Microsystems Engineering (IMTEK) at University of Freiburg.
Continue reading “Congratulations to Prof. Alwin Daus”Near perfect particle-hole symmetry in graphene quantum dots
Researchers at RWTH Aachen University and Forschungszentrum Jülich have uncovered important characteristics of double quantum dots in bilayer graphene, an increasingly promising material for possible applications in quantum technologies. The team has demonstrated near-perfect particle-hole symmetry in graphene quantum dots, which could lead to more efficient quantum information processing. The study has been published in Nature.