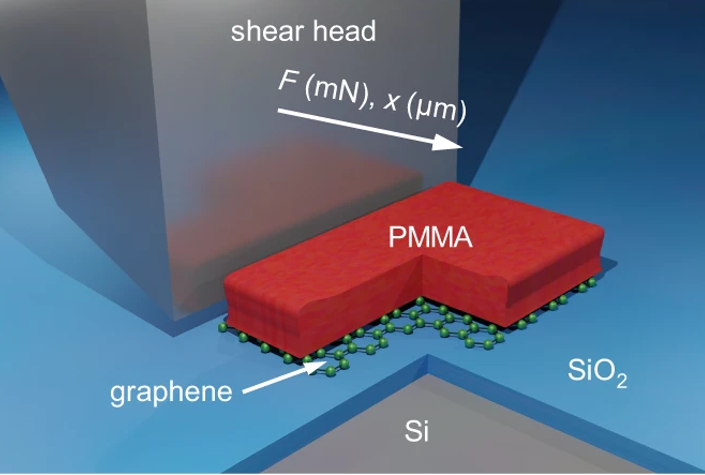
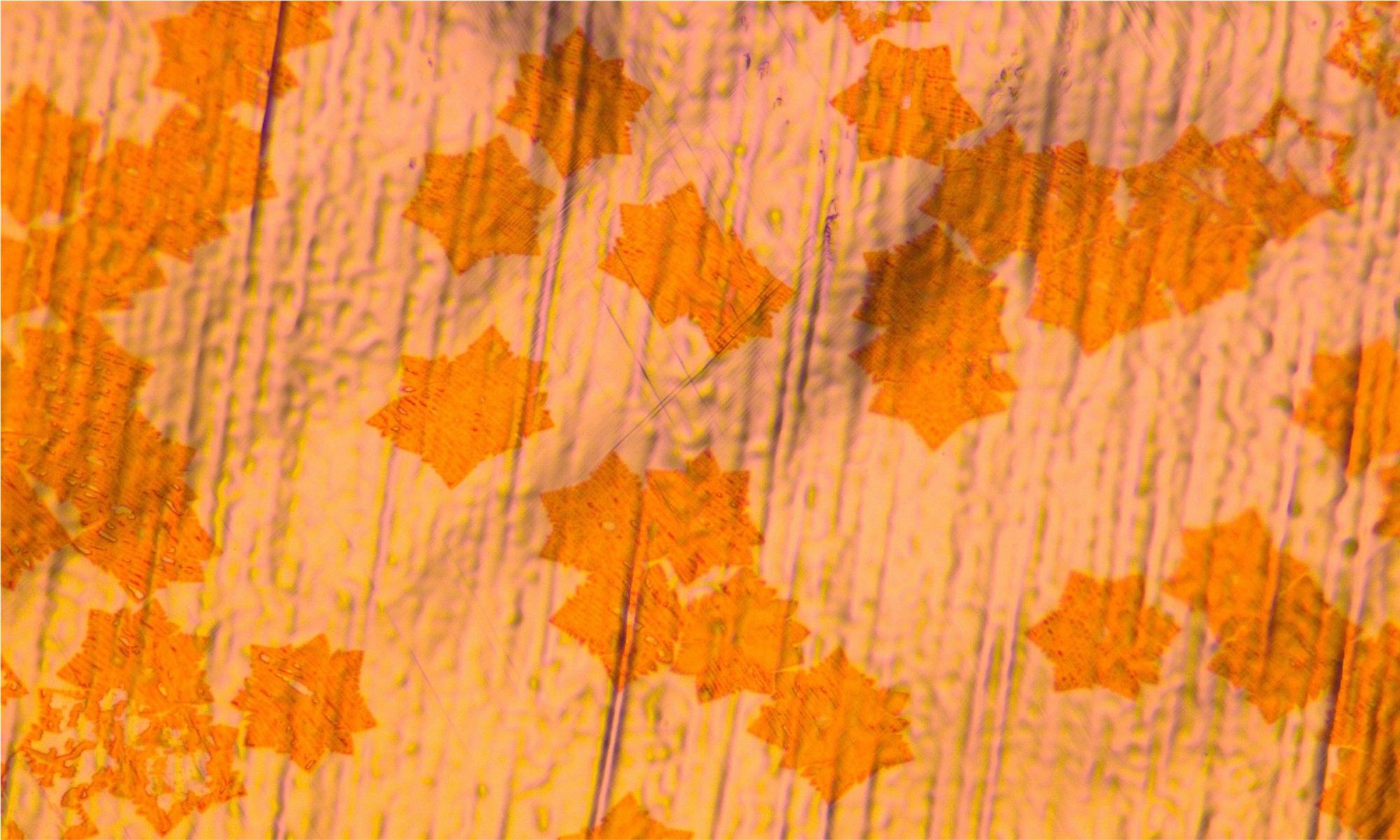
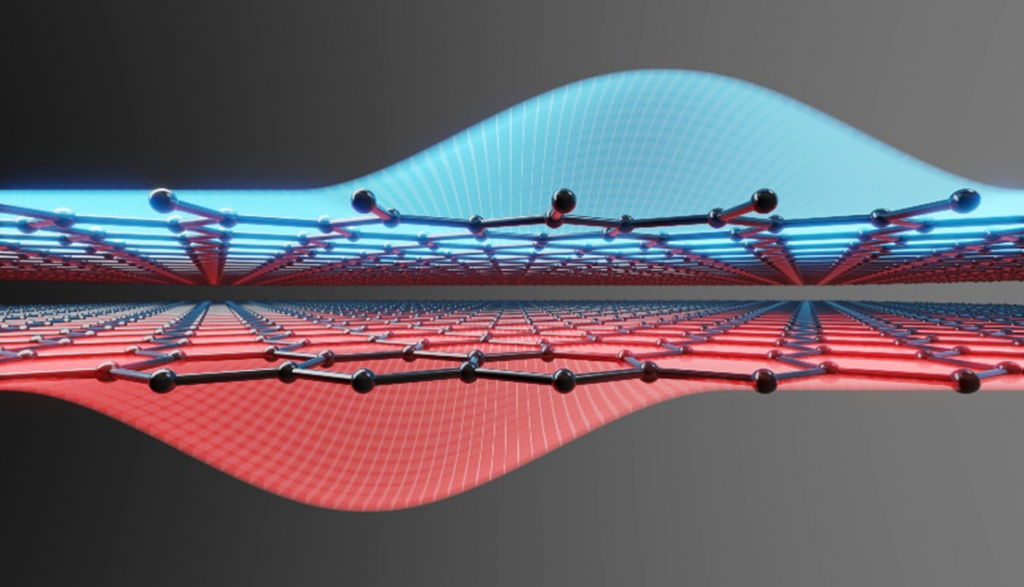
One of the big selling points of two-dimensional (2D) materials is their self-passivated nature, which allows them to be deposited on any substrate and opens up new possibilities for three-dimensional material stacks. The downside is their weak adhesion to the substrate, which can be a source of device instability. Quantifying the adhesion of 2D materials to three-dimensional surfaces is therefore an essential step for the reliable integration of devices based on 2D materials. A team of researchers around Max Lemme has now shown that the adhesion between 2D materials and substrates can be efficiently quantified using button-shear testing.